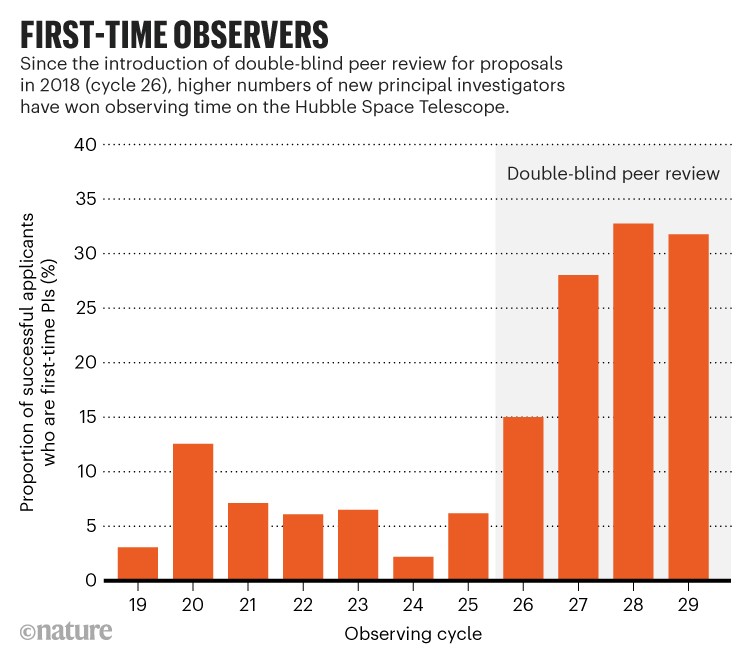
Double-blind telescope time
An unprecedented number of first-time investigators have secured viewing time on NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope in the years since the agency overhauled the application process to reduce systemic biases. In 2018, NASA changed the way it evaluates requests for observing time on Hubble by introducing a ‘double-blind’ system, in which neither the applicants nor the reviewers assessing their proposals know each other’s identities. All the agency’s other telescopes followed suit the next year. The move was intended to cut discrimination on the basis of gender and other factors, including bias against scientists who are at small research institutions, or who haven’t received NASA grants before. Data from the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, which manages Hubble, show that since the change was introduced, more first-time principal investigators have been securing viewing time on Hubble.
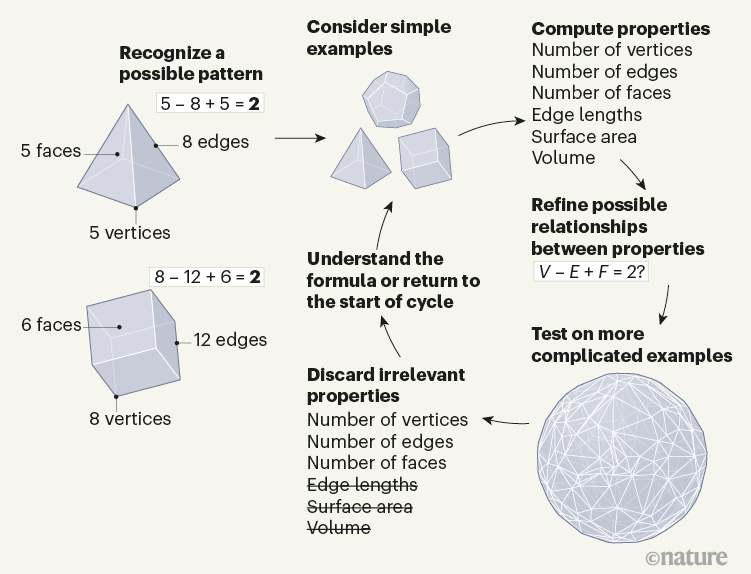
This mathematician is an AI
How do mathematicians come up with new theories? Writing in Nature, researchers describe a way of using artificial intelligence (AI) to help with the creative core of the process. After recognizing a possible pattern in the properties of mathematical objects, such as convex polyhedra (3D shapes with flat faces, straight edges and vertices that all point outwards), mathematicians typically go through a cycle to understand this pattern. They first compute the properties of some simple examples and analyse the possible relationships between these properties. They then refine the relationships. For example, they might come up with Euler’s polyhedron formula, which posits that the number of vertices (V) minus the number of edges (E) plus the number of faces (F) of a convex polyhedron is always equal to two: V − E + F = 2. They then test this suggested relationship on more complicated examples, discard irrelevant properties and attempt to understand why the relationship holds. If it remains unclear, mathematicians then consider different examples, and the cycle continues. Researchers have now shown that machine-learning techniques can help with the refinement step, which usually relies strongly on human intuition.
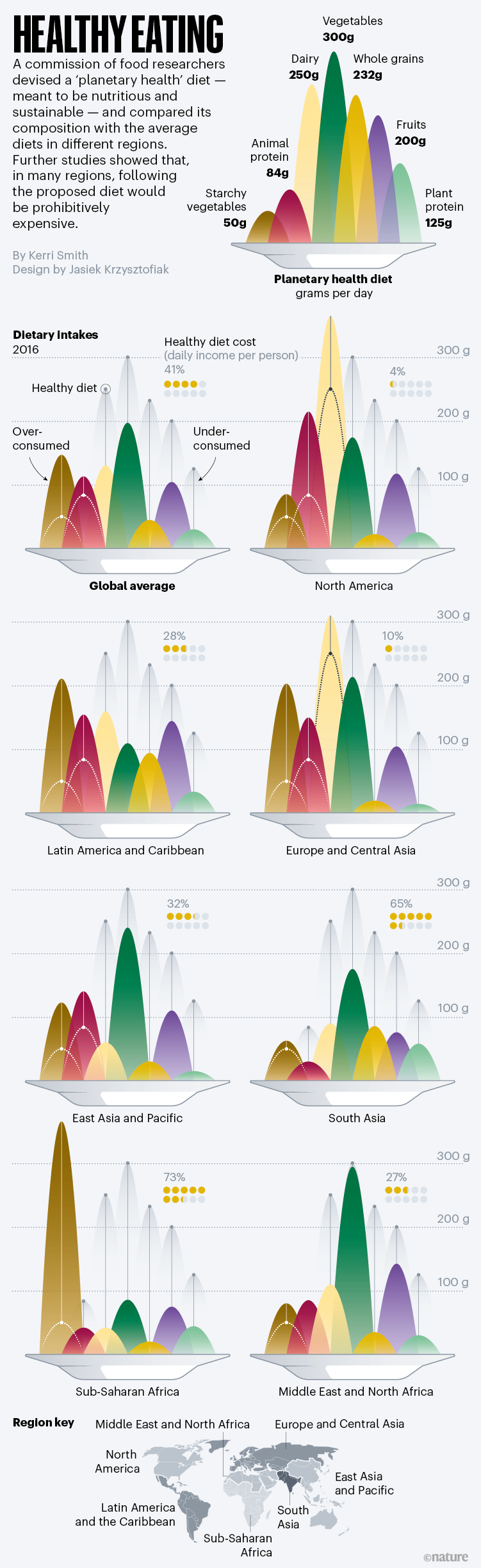
A diet to save the planet
More than 2 billion people are overweight or obese, mostly in the Western world, and 811 million are not getting enough calories or nutrition, mostly in low- and middle-income nations. At the same time, the current industrialized food system emits about one-quarter of the world’s greenhouse-gas emissions, and has other environmental impacts — which look set to rise as the world’s population increases and more people start to eat like Westerners. With both problems in mind, nutritionists reviewed the literature to craft a basic healthy diet composed of whole foods. Then the team set environmental limits for the diet, including carbon emissions, biodiversity loss and the use of fresh water, land, nitrogen and phosphorus. They ended up with a diverse and mainly plant-based meal plan that was meant to be nutritious and sustainable — a ‘planetary health’ diet. However, further studies showed that, owing to costs, switching to that diet would not be possible in many regions of the world.
"and" - Google News
December 03, 2021 at 08:24PM
https://ift.tt/3lwqCcA
AI mathematician and a planetary diet — the week in infographics - Nature.com
"and" - Google News
https://ift.tt/35sHtDV
https://ift.tt/2ycZSIP
And
Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "AI mathematician and a planetary diet — the week in infographics - Nature.com"
Post a Comment